Perception Pick & Place
Published:
Given a cluttered tabletop scenario, perform object segmentation on 3D point cloud data using python-pcl to leverage the power of the Point Cloud Library, then identify target objects from a “Pick-List” in a particular order, pick up those objects and place them in corresponding drop boxes.
Github repo https://github.com/gwwang16/RoboND-Perception-Project
Project: Perception Pick & Place
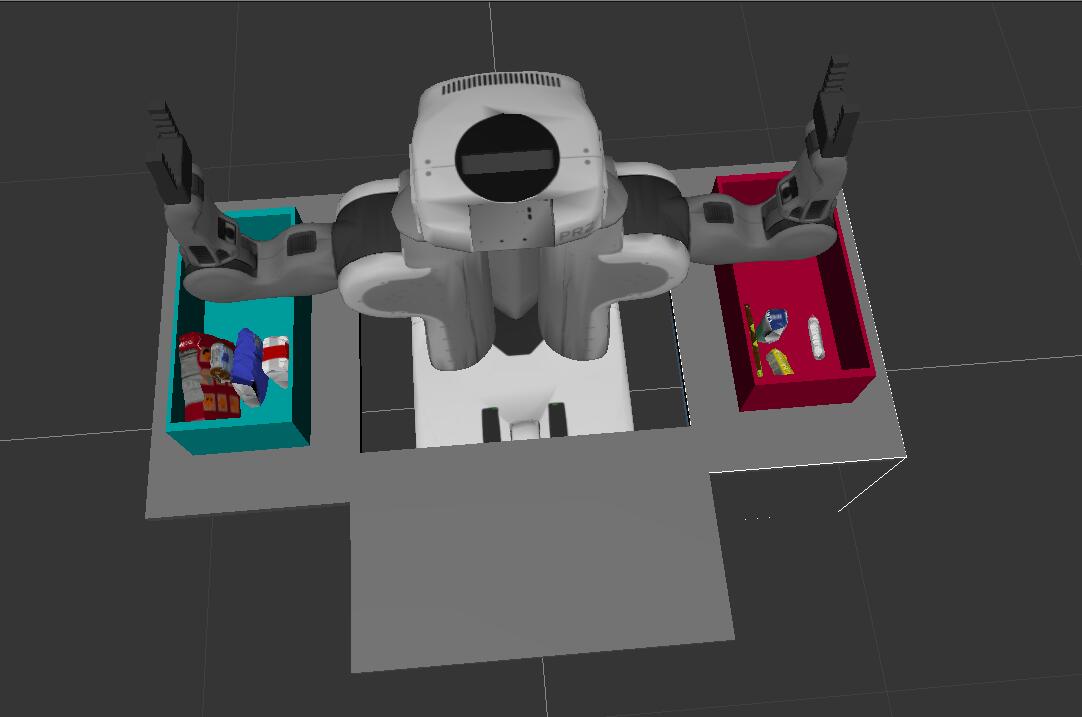
Features:
- Extract features and train an SVM model on required objects.
- Use filtering and RANSAC plane fitting to isolate the objects of interest from the rest of the scene.
- Apply Euclidean clustering to create separate clusters for individual items.
- Perform object recognition on these objects and assign them labels (markers in RViz).
- Calculate the centroid (average in x, y and z) of the set of points belonging to that each object.
- Create ROS messages containing the details of each object (name, pick_pose, etc.) and write these messages out to
.yamlfiles. - Create a collision map in rviz, allowing the robot to plan its trajectory.
- Place all the objects from pick list in their respective dropoff box.
Pipeline implemented
1. Pipeline for filtering and RANSAC plane fitting implemented.
- Statistical Outlier Filtering Set the number of neighboring points 5 and threshold scale factor 0.1, any points with mean distance larger than (mean distance+x*std_dev ) will be considered as outlier.
# Statistical Outlier Filtering # Create statistical outlier filter object outlier_filter = cloud.make_statistical_outlier_filter() # Set the number of neighboring points outlier_filter.set_mean_k(5) # Set threshold scale factor x = 0.1 # Mean distance larger than (mean distance+x*std_dev) will be considered as outlier outlier_filter.set_std_dev_mul_thresh(x) cloud_filtered = outlier_filter.filter() - Downsampling voxel grid
LEAF_SIZEis set as 0.005# Voxel Grid Downsampling # Create a voxelgrid filter object for our input point cloud vox = cloud_filtered.make_voxel_grid_filter() # Choose a voxel size (leaf size) LEAF_SIZE = 0.005 # Set the voxel size vox.set_leaf_size(LEAF_SIZE, LEAF_SIZE, LEAF_SIZE) cloud_filtered = vox.filter() - PassThrough Filter Create Passthrough filter in y and z axes
# PassThrough Filter in z axis passthrough = cloud_filtered.make_passthrough_filter() # Assign axis and range to the passthrough filter object filter_axis = 'z' passthrough.set_filter_field_name(filter_axis) axis_min = 0.6 axis_max = 1.0 passthrough.set_filter_limits(axis_min, axis_max) # Finally use the filter function to obtain the resultant point cloud. cloud_filtered = passthrough.filter() # PassThrough Filter in y axis passthrough_y = cloud_filtered.make_passthrough_filter() # Assign axis and range to the passthrough filter object filter_axis = 'y' passthrough_y.set_filter_field_name(filter_axis) axis_min = -0.5 axis_max = 0.5 passthrough_y.set_filter_limits(axis_min, axis_max) # Finally use the filter function to obtain the resultant point cloud. cloud_filtered = passthrough_y.filter() - RANSAC Plane Segmentation
# RANSAC Plane Segmentation # Create the segmentation object seg = cloud_filtered.make_segmenter() # Set the model you wish to fit seg.set_model_type(pcl.SACMODEL_PLANE) seg.set_method_type(pcl.SAC_RANSAC) # Max distance for a point to be considered fitting the model max_distance = 0.01 seg.set_distance_threshold(max_distance) # Call the segment function to obtain set of inlier indices and model coefficients inliers, coefficients = seg.segment() # Extract inliers and outliers cloud_table = cloud_filtered.extract(inliers, negative=False) cloud_objects = cloud_filtered.extract(inliers, negative=True)
2. Pipeline including clustering for segmentation implemented.
# Euclidean Clustering
white_cloud = XYZRGB_to_XYZ(cloud_objects)
tree = white_cloud.make_kdtree()
# Create a cluster extraction object
ec = white_cloud.make_EuclideanClusterExtraction()
# Set tolerances for distance threshold
# as well as minimum and maximum cluster size (in points)
ec.set_ClusterTolerance(0.01)
ec.set_MinClusterSize(100)
ec.set_MaxClusterSize(3000)
# Search the k-d tree for clusters
ec.set_SearchMethod(tree)
# Extract indices for each of the discovered clusters
cluster_indices = ec.Extract()
# Create Cluster-Mask Point Cloud to visualize each cluster separately
# Assign a color corresponding to each segmented object in scene
cluster_color = get_color_list(len(cluster_indices))
color_cluster_point_list = []
for j, indices in enumerate(cluster_indices):
for i, indice in enumerate(indices):
color_cluster_point_list.append([white_cloud[indice][0],
white_cloud[indice][1],
white_cloud[indice][2],
rgb_to_float(cluster_color[j])])
# Create new cloud containing all clusters, each with unique color
cluster_cloud = pcl.PointCloud_PointXYZRGB()
cluster_cloud.from_list(color_cluster_point_list)
# Convert PCL data to ROS messages
ros_pcl_objects = pcl_to_ros(cloud_objects)
ros_pcl_table = pcl_to_ros(cloud_table)
ros_cluster_cloud = pcl_to_ros(cluster_cloud)
# Publish ROS messages
pcl_objects_pub.publish(ros_pcl_objects)
pcl_table_pub.publish(ros_pcl_table)
pcl_cluster_pub.publish(ros_cluster_cloud)
# Create collision point
collision_point = {}
collision_point["table"] = cloud_table.to_array()
collision_point_pub.publish(ros_pcl_table)
3. Features extracted and SVM trained. Object recognition implemented.
- Features extracted
# Classify the clusters! (loop through each detected cluster one at a time)
detected_objects_labels_all = []
detected_objects_all = []
detected_objects_labels = []
detected_objects = []
for index, pts_list in enumerate(cluster_indices):
# Grab the points for the cluster
pcl_cluster = cloud_objects.extract(pts_list)
ros_cluster = pcl_to_ros(pcl_cluster)
# Compute the associated feature vector
chists = compute_color_histograms(ros_cluster, using_hsv=True)
normals = get_normals(ros_cluster)
nhists = compute_normal_histograms(normals)
feature = np.concatenate((chists, nhists[:1]))
# Make the prediction
prediction = clf.predict(scaler.transform(feature.reshape(1,-1)))
label = encoder.inverse_transform(prediction)[0]
detected_objects_labels.append(label)
# Publish a label into RViz
label_pos = list(white_cloud[pts_list[0]])
label_pos[2] += .4
object_markers_pub.publish(make_label(label,label_pos, index))
# Add the detected object to the list of detected objects.
do = DetectedObject()
do.label = label
do.cloud = ros_cluster
detected_objects.append(do)
# Add the detected object to the collision map
# collision_point[label] = pcl_cluster.to_array()
if not any(item.label == label for item in detected_objects_all):
detected_objects_all.append(do)
detected_objects_labels_all.append(label)
SVM trained
In
features.py(sensor_stick/src/sensor_stick):64 bins with range (0, 256) to compute color histograms,
3 bins with range (-1, 1) to compute normal histograms.
in
pick_list_3.yaml(src/RoboND-Perception-Project/pr2_robot/config):50 features were captured for each object to train SVM classifier.
LinearSVCclassifier is adopted here, in whichl2regularization method is used to avoid over fitting problem
clf = svm.LinearSVC(penalty='l2', loss='squared_hinge', dual=False, tol=1e-4)
scores = cross_validation.cross_val_score(cv=kf, estimator=clf,
X=X_train, y=y_train,
scoring='r2')
r2 accuracy scoring is used in cross_val_score() to increase accuracy.
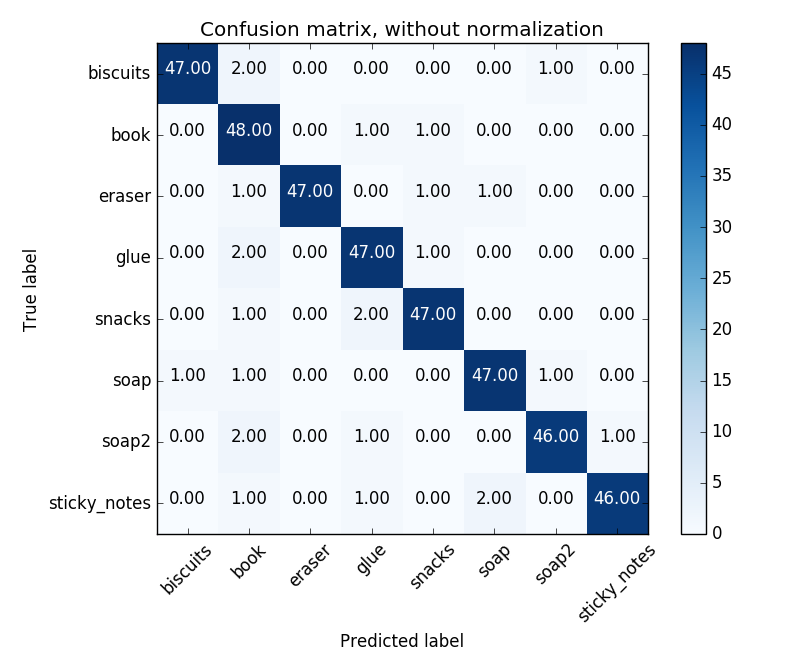
The confusion matrix without normalization is
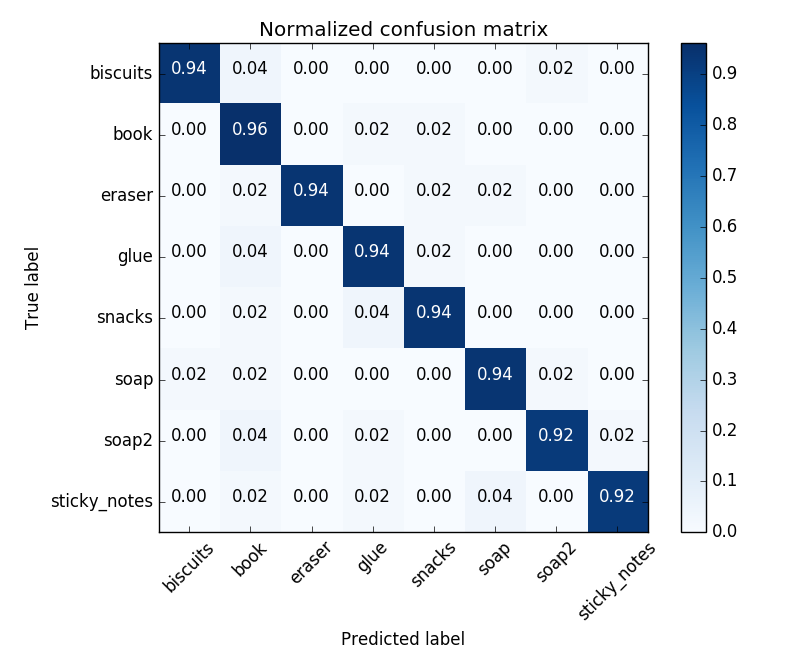
The normalized confusion matrix is
Object recognition
Variables Initialization
dict_list = [] labels = [] centroids = [] object_list_param = [] dropbox_param = [] pick_position = [] dropbox_position = [] test_scene_num = Int32() object_name = String() arm_name = String() pick_pose = Pose() place_pose = Pose() test_scene_num.data = 3
Read objects and dropbox params from yaml files
object_list_param = rospy.get_param('/object_list')
dropbox_param = rospy.get_param('/dropbox')
Loop through each object in the pick list, and ten assign the arm and ‘place_pose’ to be used for pick_place, create a list of dictionaries for later output to yaml file.
# Loop through the pick list
target_count_left = 0
target_count_right = 0
for target in object_list:
labels.append(target.label)
points_arr = ros_to_pcl(target.cloud).to_array()
pick_position = np.mean(points_arr, axis=0)[:3]
pick_pose.position.x = np.float(pick_position[0])
pick_pose.position.y = np.float(pick_position[1])
pick_pose.position.z = np.float(pick_position[2])
centroids.append(pick_position[:3])
object_name.data = str(target.label)
# Assign the arm and 'place_pose' to be used for pick_place
for index in range(0, len(object_list_param)):
if object_list_param[index]['name'] == target.label:
object_group = object_list_param[index]['group']
for ii in range(0, len(dropbox_param)):
if dropbox_param[ii]['group'] == object_group:
arm_name.data = dropbox_param[ii]['name']
dropbox_position = dropbox_param[ii]['position']
dropbox_x = -0.1 #dropbox_position[0]
# Add olace pose bias for each object
if arm_name.data == 'right':
dropbox_y = dropbox_position[1] - 0.10 + target_count_right*0.1
else:
dropbox_y = dropbox_position[1] - 0.10 + target_count_left*0.03
dropbox_z = dropbox_position[2] + 0.1
place_pose.position.x = np.float(dropbox_x)
place_pose.position.y = np.float(dropbox_y)
place_pose.position.z = np.float(dropbox_z)
# Create a list of dictionaries for later output to yaml format
yaml_dict = make_yaml_dict(test_scene_num, arm_name, object_name, pick_pose, place_pose)
dict_list.append(yaml_dict)
Pick and Place Setup
1. For all three tabletop setups (test*.world), perform object recognition, then read in respective pick list (pick_list_*.yaml). Next construct the messages that would comprise a valid PickPlace request output them to .yaml format.
- Output request parameters into output yaml file
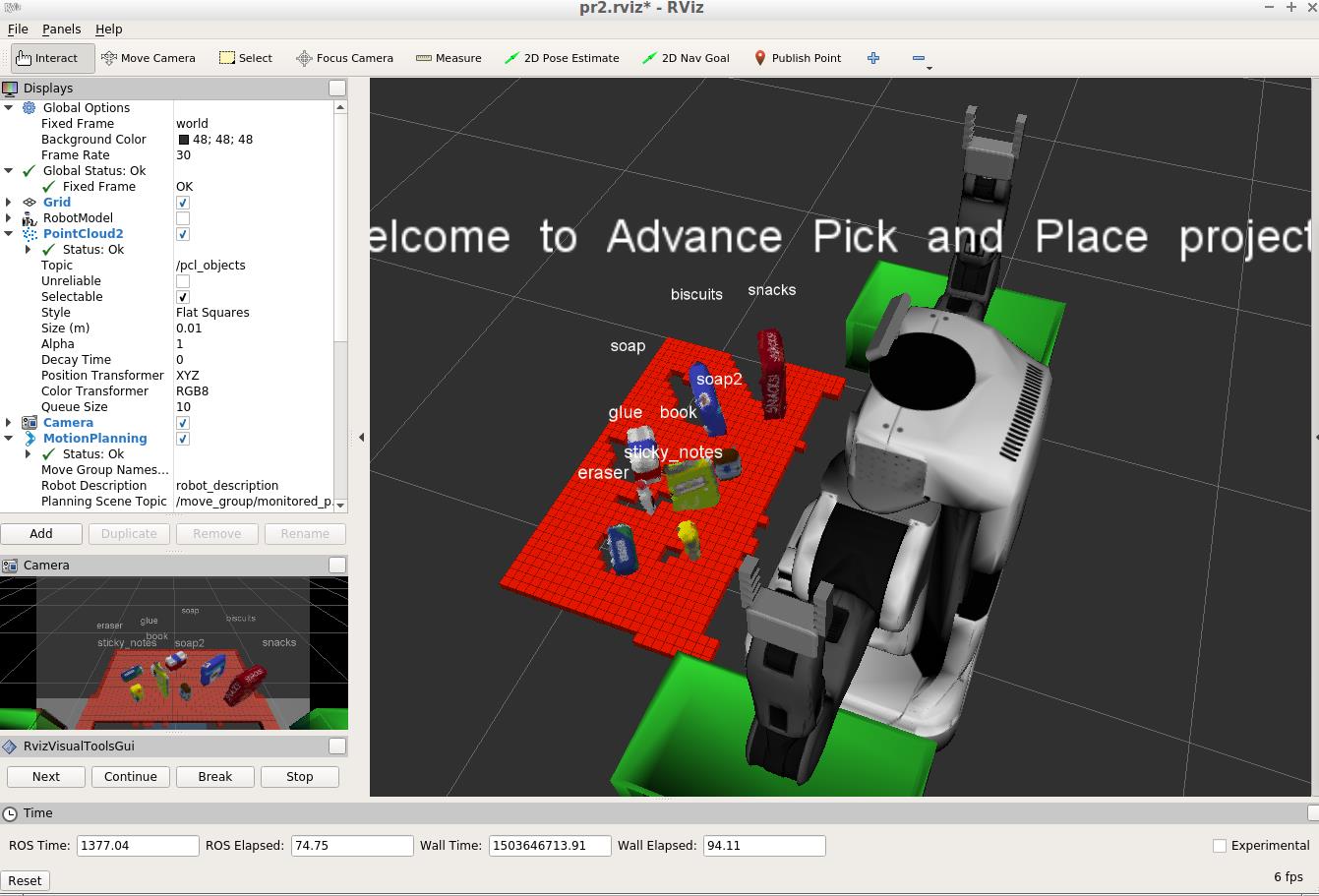
yaml_filename = 'output_' + str(test_scene_num.data) + '.yaml' if not os.path.exists(yaml_filename): send_to_yaml(yaml_filename, dict_list) Object recognition results
all objects in
pick_list_*.yamlare correctly recognized, as shown in following.
Pick & place:
1. Create a collision map and published a point cloud to the /pr2/3d_map/points topic, changed the point_cloud_topic to /pr2/3d_map/points in sensors.yaml in the /pr2_robot/config/ directory.
- To generate collision map, I built a dictionary and stored table cloud it firstly.
# Create collision point collision_point = {} collision_point["table"] = cloud_table.to_array()- Then I stored each object into the dictionary.
# Add the detected object to the collision map
collision_point[label] = pcl_cluster.to_array()
- To update the collision map, we need clear the collision map before publishing. As advised by @chedanix in slack, first calling
rostopic info /pr2/3d_map/pointsand followed byrosnode info /move_group, we can find/clear_octomapservice.from std_srvs.srv import Empty rospy.wait_for_service('/clear_octomap') try: collision_map_prox = rospy.ServiceProxy('/clear_octomap', Empty()) resp = collision_map_prox() except rospy.ServiceException, e: print "Service call failed: %s" % e - Delete the current object from collision map during picking them, publish the collision map again.
# Delete the target clound from collision map del collision_point[target.label] # Creating collision map points_list = np.empty((0,4), float) for index, target_pts in collision_point.iteritems(): points_list = np.append(points_list, target_pts[:,:4], axis=0) collision_cloud = pcl.PointCloud_PointXYZRGB() collision_cloud.from_list(np.ndarray.tolist(points_list)) collision_point_pub.publish(pcl_to_ros(collision_cloud))The collision map looks like the following
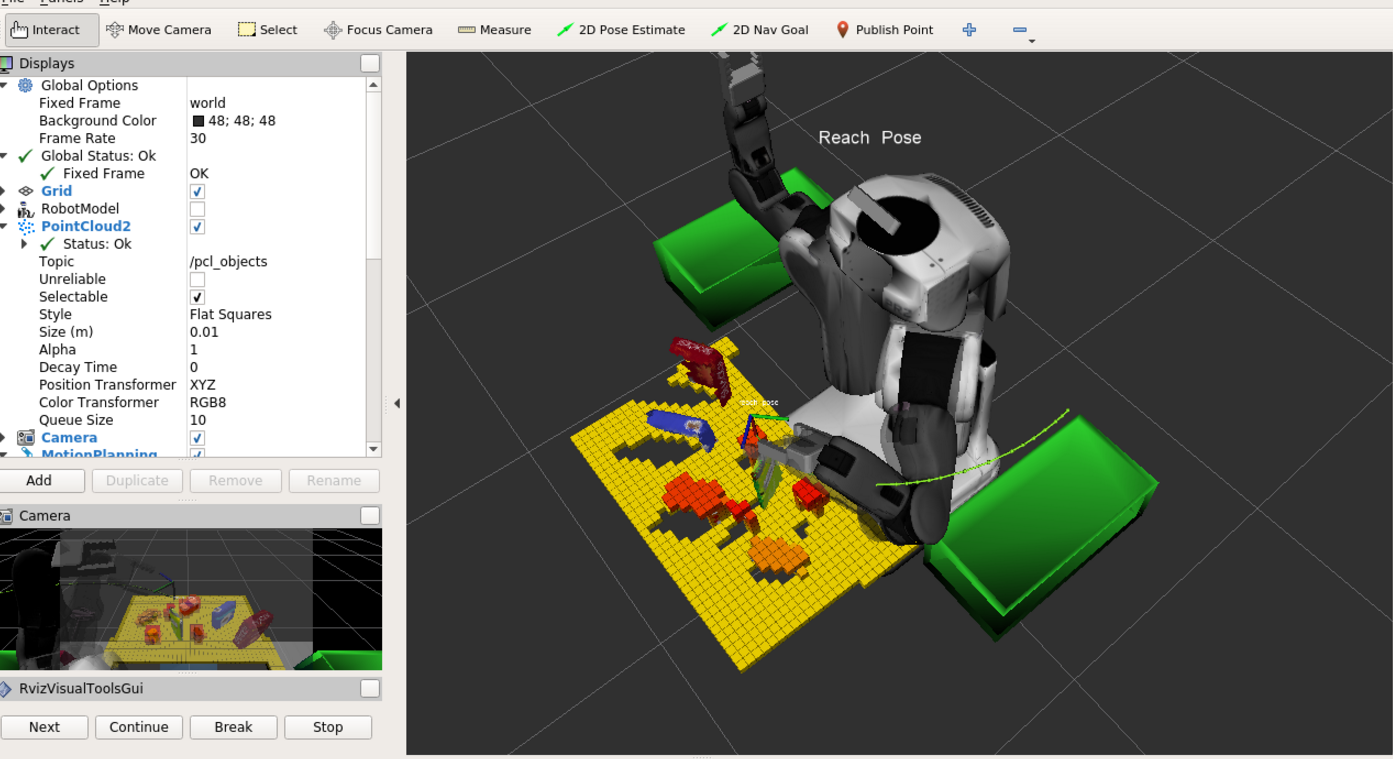
2. built pr2_rot() to rotate the robot and then back to its initial position. However, I didn’t try the challenge.world and my collision map has problem of updating, this function didn’t used.
def pr2_mov(rad):
'''move pr2 world joint to desired angle (rad)'''
rate = rospy.Rate(50) # 50hz
world_joint_pub.publish(rad)
rate.sleep()
joint_state = rospy.wait_for_message('/pr2/joint_states', JointState)
return joint_state.position[19]
def pr2_rot():
''' rotate pr2 right and left to detect environment'''
global rotation_state
global rot_dir
if rotation_state:
if rot_dir == 'left':
world_joint_state = pr2_mov(1.57)
if np.abs(world_joint_state - 1.57) < 0.1:
rot_dir = 'right'
print("Get left side, go to right side now...")
if rot_dir == 'right':
world_joint_state = pr2_mov(-1.57)
if np.abs(world_joint_state + 1.57) < 0.1:
rot_dir = 'center'
print("Get right side, go to center now...")
if rot_dir == 'center':
world_joint_state = pr2_mov(0)
if np.abs(world_joint_state) < 0.1:
rotation_state = False
print("Get center, exist rotation.")
3. There are some problems during objects grasping. To solve this problem, I added fraction coefficients for each item intest1-3.world (/pr2_robot/worlds)
<model name='snacks'>
<collision name='snacks_collision'>
<pose frame=''>0.04 0.02 0.117 0 -0 2.1</pose>
<geometry>
...
</geometry>
<max_contacts>10</max_contacts>
<surface>
<contact>
<ode/>
</contact>
<bounce/>
<friction>
<torsional>
<ode/>
</torsional>
<ode mu="1.0" mu2="1.0" fdir1="0 0 1"/>
</friction>
</surface>
</collision>
...
</model>
Reference:
http://gazebosim.org/tutorials/?tut=ros_urdf
http://www.ode.org/ode-latest-userguide.html#sec_7_3_7
As for my collision map cannot be updated once it was published, so I used table cloud as collision map only. The consequence is the gripper would hit other objects during grasping one. So I increased a bit drop position height to avoid this problem. To arrange the picked objects, I added a bias in y axis for each drop position.
# Assign the arm and 'place_pose' to be used for pick_place
for index in range(0, len(object_list_param)):
if object_list_param[index]['name'] == target.label:
object_group = object_list_param[index]['group']
for ii in range(0, len(dropbox_param)):
if dropbox_param[ii]['group'] == object_group:
arm_name.data = dropbox_param[ii]['name']
dropbox_position = dropbox_param[ii]['position']
dropbox_x = -0.1 #dropbox_position[0]
# Add olace pose bias for each object
if arm_name.data == 'right':
dropbox_y = dropbox_position[1] - 0.10 + target_count_right*0.1
else:
dropbox_y = dropbox_position[1] - 0.10 + target_count_left*0.03
dropbox_z = dropbox_position[2] + 0.1
place_pose.position.x = np.float(dropbox_x)
place_pose.position.y = np.float(dropbox_y)
place_pose.position.z = np.float(dropbox_z)
if resp.success:
if arm_name.data == 'right':
target_count_right += 1
if target_count_right == 3:
arget_count_right = 0.5
else:
target_count_left += 1
4. all objects are placed into their respective drop box. Results are the following.


Leave a Comment